Rooftop photovoltaics – How they work and what to expect

A photovoltaic or solar power plant produces electricity from the sun's radiation. It is a renewable and inexhaustible energy source that does not require any fuel to generate electricity.
A photovoltaic power plant consists of two basic components – photovoltaic (solar) panels and an inverter.
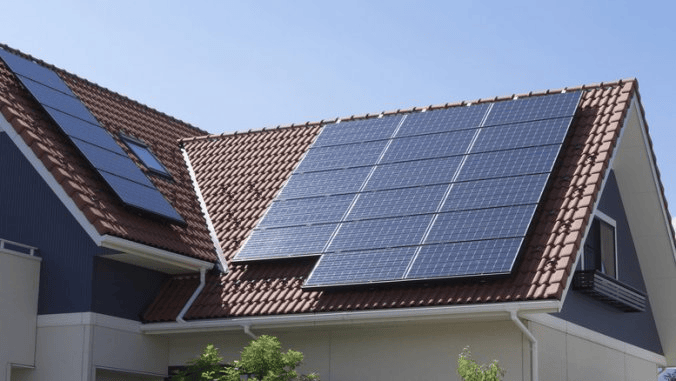
Photovoltaic panels – They produce electricity when sufficiently illuminated, specifically direct current. The panels can be placed on the roof of a house, garage, pergola, or even on a façade, as well as on the roof of a production hall, the roof of a parking lot or on a plot of land. The more panels that are installed, and the longer they are exposed to the sun, the more power the plant provides.
Inverter, Converter (both terms are valid) – In order to utilize the electricity produced by photovoltaics, it is necessary to connect an inverter to the panels. The inverter converts DC current from the panels into alternating current electricity, which standard appliances connected to a socket require. The inverter usually looks like a "box on a wall" that receives electricity from the panels via a series of cables. Only the inverter supplies electricity via a cable to the fuse box in the home or company.
If you wish to utilize energy from the sun, even when the sun is not shining, which is typically at night, it is necessary to connect some kind of medium to store the energy – most often an electric battery or a hot water tank. If the storage medium is not sufficient during times without sunlight, the photovoltaics need to be supplemented with a backup source of electricity. This can be a petrol or diesel powered unit, a co-generation unit, a fuel cell, or even a conventional electrical connection.